 C[c] is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains widely used and influential. By design, C gives the programmer relatively direct access to the features of the typical CPU architecture, customized for the target instruction set.
C[c] is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains widely used and influential. By design, C gives the programmer relatively direct access to the features of the typical CPU architecture, customized for the target instruction set. The C Programming Language has often been cited as a model for technical writing, with reviewers describing it as having clear presentation and concise treatment.
The C Programming Language has often been cited as a model for technical writing, with reviewers describing it as having clear presentation and concise treatment.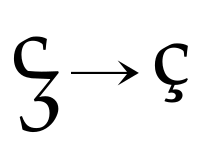 Ç or ç (C-cedilla) is a Latin script letter used in the Albanian, Azerbaijani, Manx, Tatar, Turkish, Turkmen, Kurdish, Kazakh, and Romance alphabets. Romance languages that use this letter include Catalan, French, Portuguese, and Occitan, as a variant of the letter C with a cedilla.
Ç or ç (C-cedilla) is a Latin script letter used in the Albanian, Azerbaijani, Manx, Tatar, Turkish, Turkmen, Kurdish, Kazakh, and Romance alphabets. Romance languages that use this letter include Catalan, French, Portuguese, and Occitan, as a variant of the letter C with a cedilla. C, or c, is the third letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide.
C, or c, is the third letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide.